Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Yusuke*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2023-003, 67 Pages, 2024/02
A long-term geosphere stability for geological disposal is evaluated by the past geological environmental changes and modern conditions. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios ( D,
D, 
 O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for
O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for  D and
D and 
 O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of
O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of  D and
D and 
 O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the
O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the  D and
D and 
 O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
 Cs to web-building spiders,
Cs to web-building spiders, 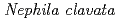 , and its pathways; A Preliminary study using stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analyses
, and its pathways; A Preliminary study using stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analysesTanaka, Sota; Kakinuma, Hotaru*; Adachi, Taro*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.507 - 514, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Understanding the pathways of  Cs transfer to predatory spiders is useful to assess long-term behavior of
Cs transfer to predatory spiders is useful to assess long-term behavior of  Cs in the environment, because spiders obtain food resources from both the grazing and detritus food chains in terrestrial-aquatic linking forest ecosystems. In the present study, we collected spider samples at forest interior and riverside. The sample collection was approximately 6.5 years after the FDNPP accident. Moreover, a transfer factor value (T
Cs in the environment, because spiders obtain food resources from both the grazing and detritus food chains in terrestrial-aquatic linking forest ecosystems. In the present study, we collected spider samples at forest interior and riverside. The sample collection was approximately 6.5 years after the FDNPP accident. Moreover, a transfer factor value (T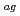 ) for
) for  Cs in spiders was quantified. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios (
Cs in spiders was quantified. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios (
 C and
C and 
 N) of the spiders were also investigated to estimate the transfer pathways of
N) of the spiders were also investigated to estimate the transfer pathways of  Cs to the spiders.
Cs to the spiders.
Konda, Miki; Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Magara, Masaaki
JAEA-Technology 2015-054, 22 Pages, 2016/03
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) with ICP-MS is reliable method for determination of Zr-93, which is one of the long-lived fission products found in spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive wastes. In order to use an isotope standard solution of zirconium as the spike for IDMS, dissolving a commercially available solid isotope standard is indispensable. Prior to the dissolution of the Zr-91 isotope standard, solubility of metal zirconium in a mixture of HNO and HF was evaluated using zirconium metal chips. Then, 2 mg of the Zr-91 isotope standard was dissolved with 0.2 mL of 1 M HNO
and HF was evaluated using zirconium metal chips. Then, 2 mg of the Zr-91 isotope standard was dissolved with 0.2 mL of 1 M HNO -3 v/v% HF mixed solution, followed by adjusting the concentration of Zr-91 to approximately 1,000
-3 v/v% HF mixed solution, followed by adjusting the concentration of Zr-91 to approximately 1,000  g/g. IDMS, in which a natural isotopic abundance standard solution of zirconium was used as the spike, was employed for the determination of the concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. The concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution was (9.6
g/g. IDMS, in which a natural isotopic abundance standard solution of zirconium was used as the spike, was employed for the determination of the concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. The concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution was (9.6 1.0)
1.0)  10
10
 g/g, which is in good agreement with the predicted concentration. This indicates that the Zr-91 metal isotope standard was completely dissolved with sufficient chemical stability. Additionally, no impurities were detected in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. These positive results denote that the Zr-91 isotope standard solution with the preferable quality for IDMS of Zr-93 can be obtained by the proposed dissolution procedures.
g/g, which is in good agreement with the predicted concentration. This indicates that the Zr-91 metal isotope standard was completely dissolved with sufficient chemical stability. Additionally, no impurities were detected in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. These positive results denote that the Zr-91 isotope standard solution with the preferable quality for IDMS of Zr-93 can be obtained by the proposed dissolution procedures.
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Naganawa, Hirochika
Journal of Water and Environment Technology (Internet), 3(2), p.243 - 252, 2005/00
In a tributary watershed of the Kuji River of Japan, the hydrological components of runoff associated with a rain storm event were investigated using isotope tracers of hydrogen ( H) and oxygen (
H) and oxygen ( O) in precipitations and stream water. The runoff was separated into either "old water" (pre-existing in the ground before the storm) and "new water"(from the storm precipitation). It was found that the discharge of several hazardous trace elements (Sb, Cu, Cr) was largely (24-54%) attributable to that of the new water in spite of its small contribution to the total water discharge. These investigations suggest that the new water may play an important role in the migration of atmospherically derived, hazardous trace elements to streams during rain storms.
O) in precipitations and stream water. The runoff was separated into either "old water" (pre-existing in the ground before the storm) and "new water"(from the storm precipitation). It was found that the discharge of several hazardous trace elements (Sb, Cu, Cr) was largely (24-54%) attributable to that of the new water in spite of its small contribution to the total water discharge. These investigations suggest that the new water may play an important role in the migration of atmospherically derived, hazardous trace elements to streams during rain storms.
Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Munakata, Masahiro; Matsumoto, Junko; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Wang, Z.*; Yang, Y.*; Zhao, Y.*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, p.179 - 184, 2003/00
Migration behaviors of stable strontium element and radioactive nuclide strontium 90 in natural aquifer were studied by a field test, which was performed in the aquifer loess zone at 30 m under the ground surface of the field test site of China Institute for Radiation Protection. The migration behavior of stable strontium was a little different from that of  Sr. The difference was evaluated by applying the distribution coefficient considering Sr and coexistent ion concentrations. Migration behavior of radionuclide in natural environment has been generally demonstrated on field tests without radioactive tracers and/or large-scale column tests with radioactive tracers. Such tests seem to be valuable to improve reliability of the migratory evaluation.
Sr. The difference was evaluated by applying the distribution coefficient considering Sr and coexistent ion concentrations. Migration behavior of radionuclide in natural environment has been generally demonstrated on field tests without radioactive tracers and/or large-scale column tests with radioactive tracers. Such tests seem to be valuable to improve reliability of the migratory evaluation.
Kushita, Kohei
JAERI-Review 2001-043, 95 Pages, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
 , CO
, CO and N
and N O in Tokai-mura
O in Tokai-muraPorntepkasemsan, B.*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Amano, Hikaru
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-032, 43 Pages, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
 O release experiement; Transfer of deutrium and Carbon-13 from air to plant
O release experiement; Transfer of deutrium and Carbon-13 from air to plantAtarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Amano, Hikaru; Porntepkasemsan, B.; Kakiuchi, Hideki; Ichimasa, Michiko*; Ichimasa, Yusuke*
KURRI-KR-53, p.18 - 21, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru; Porntepkasemsan, B.; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Kushita, Kohei
KURRI-KR-53, p.6 - 9, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru; Porntepkasemsan, B.; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Kushita, Kohei
KURRI-KR-53, p.6 - 9, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Isotope News, 0(483), p.38 - 39, 1994/09
no abstracts in English
Sep.Sci.Technol., 17(8), p.1049 - 1064, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:85.26(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
;
Bunseki Kagaku, 23(7), p.804 - 810, 1974/07
no abstracts in English
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 12(7), p.424 - 425, 1970/00
no abstracts in English

 C,
C, 
 N)
N)Tanaka, Sota; Kakinuma, Hotaru*; Adachi, Taro*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun
no journal, ,
Terrestrial arthropods could be an indicator species of long-term behavior of radiocesium through the food chain due to their large biomass and importance as food resources for other organisms. The spider, Nephila clavata, as generalist predators is especially suggested that an indicator species of radiocesium contamination of insect communities because they prey on variety of food resources from both grazing and detrital food chain. In present study, the aggregated transfer factor (T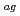 ) of
) of  Cs for the spiders inhabited at mountainous forest and riverside was calculated using the initial deposition densities map, and stable isotope ratio(
Cs for the spiders inhabited at mountainous forest and riverside was calculated using the initial deposition densities map, and stable isotope ratio(
 C,
C, 
 N) of the spider was measured to determine the transfer pathway of
N) of the spider was measured to determine the transfer pathway of  Cs.
Cs.